Thallophyta ( plant kingdom ) , plantae: classification
Thallophyta
- These are the plants with no body differentiation
- They do have a specific root, stem, leaves so they do not have specific differentiation
- They prefer aquatic habitats
examples :-green algae - In thallophyta they have a hidden reproductive system -cryptogamae
Algae
- They are autotrophic
- Habitat :-
Mostly aquatic (freshwater/ marine ) , found in most soil/ wood - Structure :- It can be unicellular,colonial, filamanteous
- Examples :-volvox ( colonial ), Chlamydomonas (unicellular ), Ulothrix (filamenteous ), Spirogyra ( filamenteous ), Ulva, Cladophora (branched filaments) it is also known as river weed
Algae reproduction
Asexual reproduction :- Fragmentation
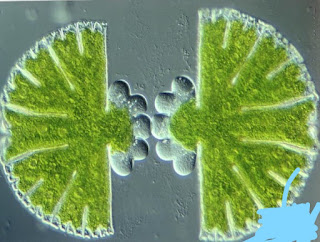
Parent organism will break into new pieces or multiple pieces on maturity, each of which give rise to a new individual. Example :- spirogyra when it becomes matures it breaks into new pieces and each of these pieces are able to give rise to a new organism altogether.
Fission
- In multiple fission many new individuals are formed
- Nucleus divides repeatedly
- It takes place during unfavourable conditions (cyst formation takes place )
Spore formation
- Production of asexual spores
Reproductive spores : zoosporangium
Asexual spores : zoospores
Sexual reproduction :-
- Fusion of two gametes
- Types :
Isogamous -Both gametes are similar in size. Ex , spirogyra
Anisogamous- Gametes are dissimilar in size
Oogamous - One gametes is large & non motile, while the other is small & motile. Ex,Volvox - One is a male gamete called anthrozoid and other is female gamete called egg, fusion takes place and results in making of zygote and spore formation takes place, so the spores will germinate and this will give rise to a new colony. so again this colony will give rise to a new colony. so this is the cycle of algae reproduction.
Significance
- Carbon dioxide fixation on earth
- It increases level of oxygen in atmosphere
- It is important source of food
- Some of them are very rich source of protein. Ex,chlorella, spirullina
- They help in preparation of ice-creams & jellies
- Agar is obtained from an algae gelidium and glacilaria which helps in making of ice-creams
Photosynthetic pigments
- Chlorophyll
-Colour green
-predominant in leaves
chlorophyll is green in colour because it absorbs red and violet colour the most in VIBGYOR but it is not able to absorbs the middle colour green colour is transmitted to us. So it is green in colour. But some are red in colour so here other colour are absorbed but red is transmitted to us. so some are in colour. - Structure- Chlorophyll a, b, c
- Carotenoids
- colour ranges from yellow to red
- Predominant in flower and fruits - Carotene : They are pure carbohydrate
- Xanthophylls ; carotenoids with oxygen( yellow )
Algae : Types
Chlorophyceae :-
- Green algae
- Autotrophic
- Habitat
-primarily freshwater
-Found in soil/tree/bark - Can be unicellular/filamenteous//colonial
- Examples: Chlamydomonas, volvox, ulothrix, spirogyra
- Structure :- Rigid 2 layered cell wall
outer layer wall : Pectin (It constitute the matrix in which cellulose microfibrils are embedded )
Inner layer wall : cellulose (It is the main load bearing structure ) - Chloroplast can be seen in different shapes in different species
- Chlorophyll a & b are present
- "pyrenoids" are present. They are the storage bodies in chloroplasts which store proteins and starch
- Life cycle :-
Isogamous/Anisogamous/Oogamous
Diploid phase : short lived
Haploid phase : dominant
Phaeophyceae :-
- Brown algae
- They can be branched/filamentous
- They prefer marine habitats
- Examples : Laminaria, Fucus, Dictyota
- Structure :-
cell wall is made up of cellulose
Its outer covering of cell is made up of Algin (it is used in preparation of foods )
-chloroplast can be seen in different shapes in different speices
-chlorophyll a, c, carotenoids and Xanthophylls present
Their brown colour is due to the presence of these pigments - Food is stored in the form of complex carbohydrates like laminarin
- Significant organelles are :-plastids, vacuole, nucleus
The structure of the plant body there are three main parts :- holdfast, stipe, frond - Life cycle :
It involves succession of haploid & diploid phases
Rhodophyceae :-
- They are red algae
- They live in marine habitat in fresh/salty water and occurs both on the surface as well as deep inside water
- Cell wall is made up of cellulose
chlorophyll a, d and phycoerythrin present - Food here is stored in the form of floridean starch
- Examples : polysiphonia, porphyra, gracilria
- Life cycle :- The life cycle of red algae is very very similar to the brown algae except that they do not have flagellated gametes. Their gametes are non flagellated.











Comments
Post a Comment